Introduction:
We use many electronic and thermodynamic devices that make our lives better than before. You all know that cooling is essential for the proper functioning of every kind of device or equipment. Cooling is necessary for almost every type of device, whether it’s a small or a large size device. The cooling process helps the devices to manage their workload evenly. Several cooling technologies can help the device’s proper functioning; one is a liquid cold plate. When air cooling is not competent to evacuate heat from the device, we can provide cooling through liquid plates.
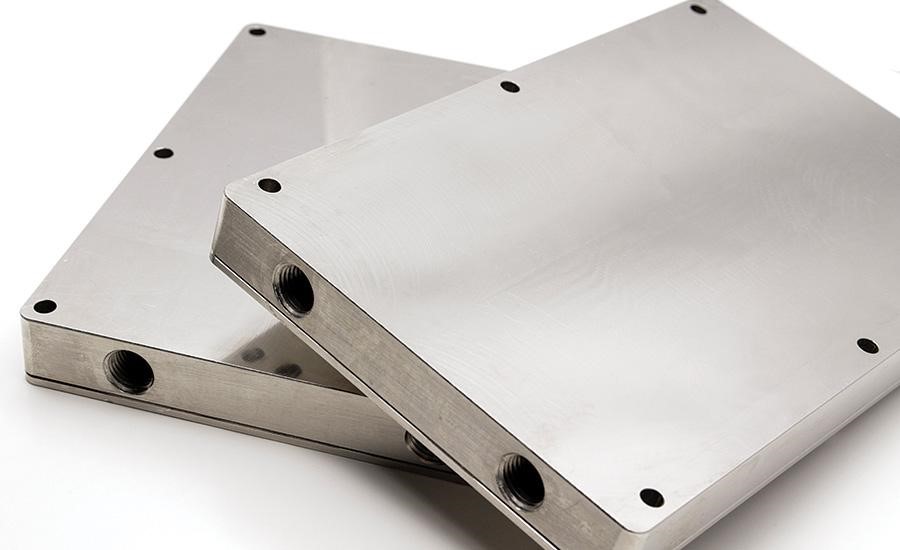

Liquid cold plates are a considerable invention in the thermal management system, which aids the device in managing the high heat flux. A liquid cold plate system is highly effective and produces good results when the air cooling system doesn’t correctly work with the device structure.
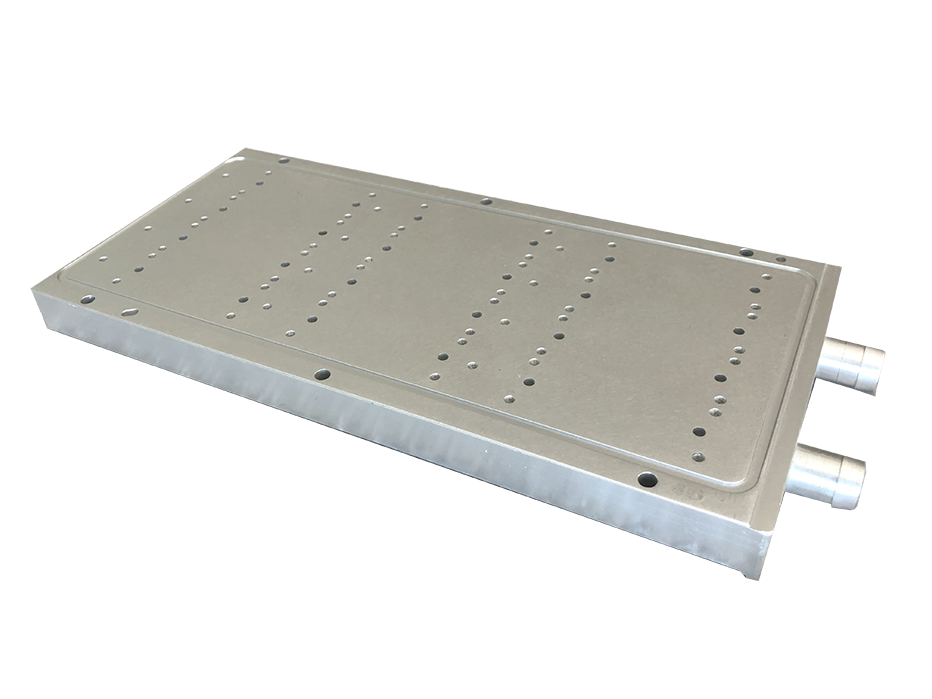

What is a Liquid Cold Plate?
Liquid cold plates are becoming the vital and foremost part of those devices whose output is very high. They need a proper cooling system that matches the device’s functioning effectively.
When air cooling is insufficient for the device, the liquid cooling system is added to the device to evacuate heat and proper functioning of high-powered machines.
The liquid cold plates act as a heat exchanger device that can remove heat derived from power semiconductors and batteries. It helps the devices to work correctly and produce effectual output.
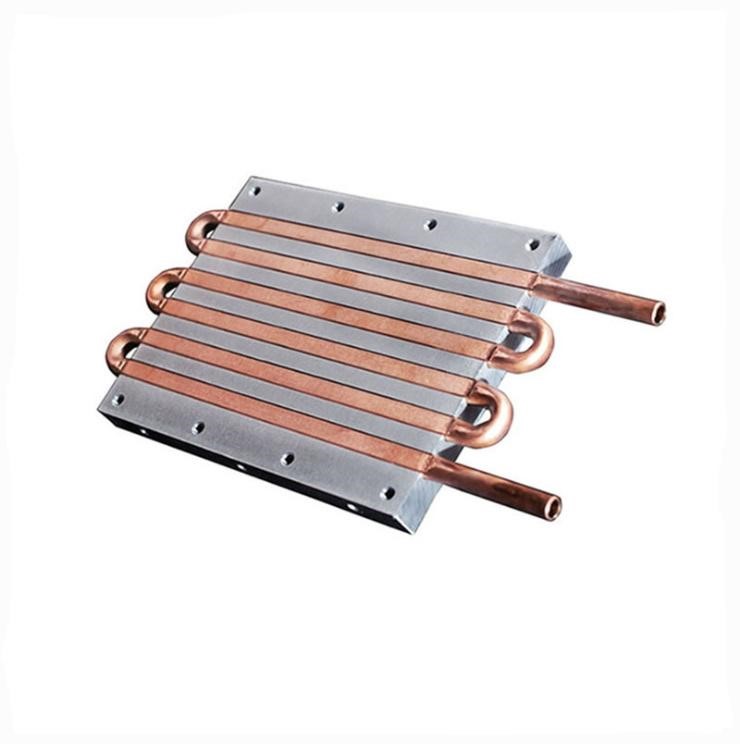

How Does A Liquid Cold Plate Work?
When air cooling fails to cope with the thermal performance of high-powered devices, then the liquid cold plate is the best choice for heat flux devices.
Liquid cold plate is a metal plate having a route for flowing the heat transfer fluid. These tubes are made from an alloy of stainless steel or copper and are coated in a cold aluminum plate.
The plate sucks exhausted heat and makes the device able to run correctly. The tubes are designed for flowing liquid, and the tubes are of different shapes and kinds according to the structure of the equipment. The fluid, flow rate, and the material used to construct a liquid cold plate all affect the heat transfer capability.
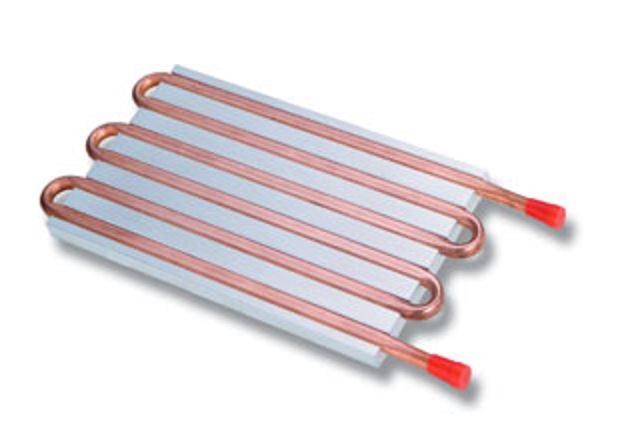
High-powered devices must evacuate heat for proper functioning, but devices are of different kinds and dimensions. So, different types of liquid cold plates are introduced to meet the functionality of different kinds of devices.
Types Of Liquid Cold Plate:
- Tube in Plate/Embedded Tube Cold Plates
- Gun Drilled Cold Plates
- FSW Friction Stir welded Cold Plates
- Die Cast Cold Plates
- Brazed Cold Plates
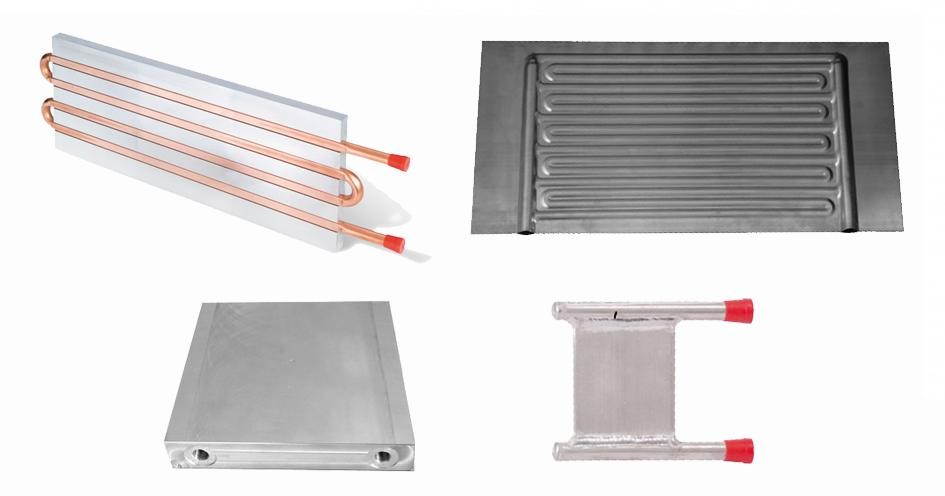

Tube in Plate/Embedded Tube Cold Plate:
It is the simplest form of the cold plate where a specific type of tube is constructed into the aluminum or copper alloy with no joint, or you can say a joint-free tube. It is dependent on the required thermal performance.
The cooling fluid that can be used in this type can be copper or stainless steel, and this can be a simple mechanical pass fit with a thermal epoxy boundary to abolish microvoids in place for maximum thermal performance.
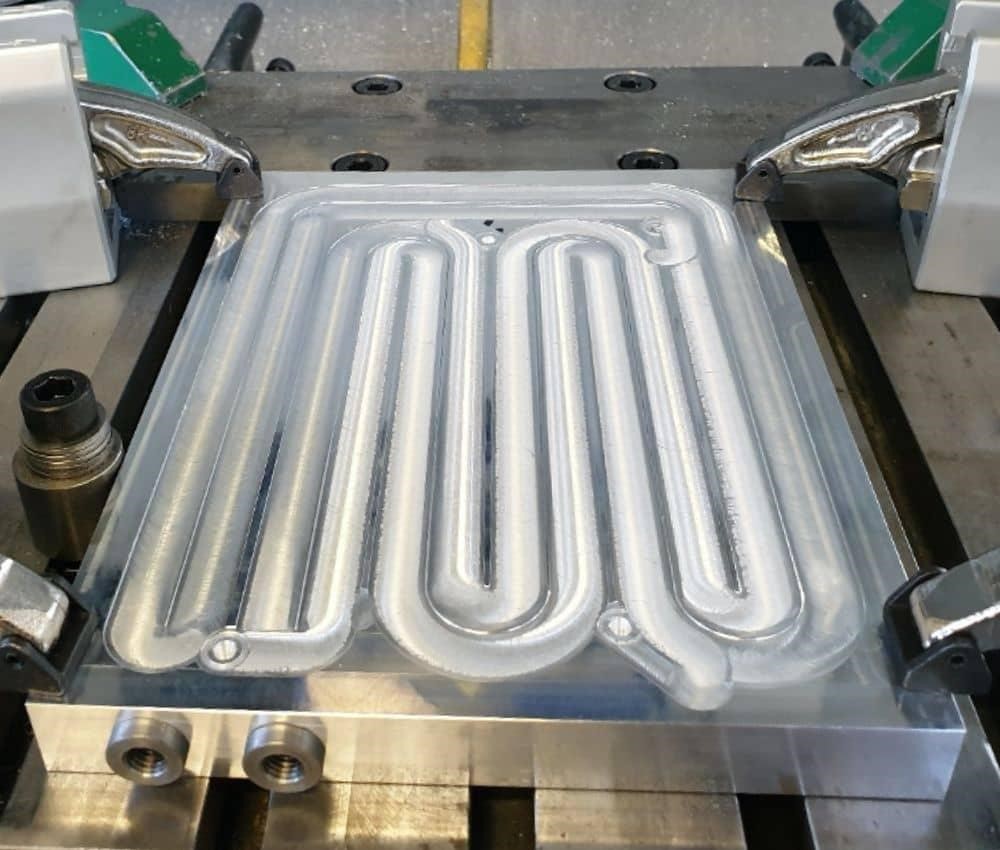
Gun Drilled Cold Plate:
A gun drilled cold plates assembled by drilling holes in a sequence through the length of an aluminum plate to form various flow paths.
For the inlet and outlet fluid paths, holes are drilled perpendicular to the main fluid path and then comparatively plugged to generate a continuous coolant path. These plates have no thermal boundaries, and the aluminium plate had no thermal stress during the assembling process. This is the excellent advantage of a gun-drilled plate.
FSW Friction Stir Welded Cold Plate:
FSW is a two-piece structure. Fluid channels are CNC machined into the base. This channel is complex and may even contain fins to improve the heat transfer surface. A profile cap is then placed in the recess above the flow path, and the F.S.W. (Friction Stir Welding) is installed in place. Finally, cut the weld face flat and add entry/exit holes and component mounting holes.

Die-cast Cold Plate:
The die-cast design has two pieces of cold plates, and tubes are constructed inside those plates.
All external and internal functions are combined in a single die-cast plate. After construction, the two halves bonded together perfectly for a productive output.
Brazed Liquid Cold Plate:
In brazed cold plates, there is the connection of two or more metals like aluminum plates by melting an alloy.
These are typically utilized in high-performance equipment that requires excellent thermal resistance. It is designed with a high-performance corrugated aluminum fin that makes the brazed liquid cold plate able to absorb maximum heat.
Vacuum Brazing Cold Plate:
It gives us consistent heating and precise temperature control that helps the devices to work evenly. As compared to other dressing, vacuum brazing Reduces the formation of components. Vacuum brazing is ideal for Aerospace Components and medical types of equipment.
Dip brazing Cold Plate:
The metals are cleaned with the help of chemicals and heated in an air furnace at a very high temperature of 1025°f to ensure uniformity.
The assembly is then submerged into a molten salt bath where molten flux connects the internal and external surfaces. Although dip brazing and vacuum brazing are made differently, both provide proper cooling for the device.
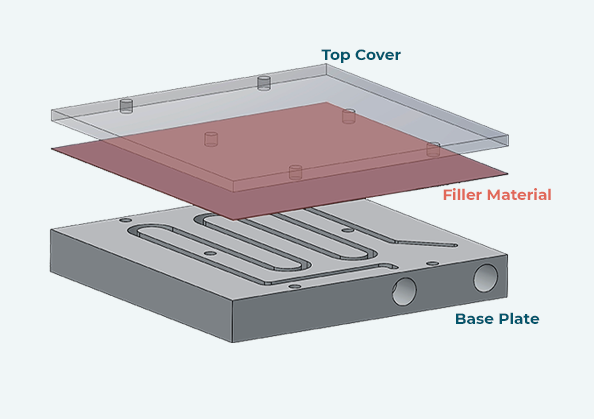
Applications of Liquid Cold Plate:
Liquid cold plates are used in those kinds of devices where the cooling of machine parts is too much necessary for the effective functioning of the whole equipment.
A liquid cold plate is mostly used for maintaining cooling in
- Batteries
- Power semiconductor systems
- Lasers
- The industrial power sector
- Power drives
- Military and Aerospace industries
- and some medical equipment

Advantages of Liquid Cold Plate:
- Evacuates maximum heat from the device
- It can manage high heat as compared to the air cooling system
- It does not affect the machine’s functioning
- The efficiency in liquid cold plates is much higher than in the traditional air cooling system
Features To Be Analyzed In Liquid Cold Plate Design:
When designing a liquid cold plate, several challenges should be overcome to create an optimal design. Following are the performance features that should be analyzed in liquid cold plate design.
- Pressure drop
- Path of liquid flow
- Flow parity
- Material compatibility
- Fluid strength
- Temperature conformity
- Extreme Temperature
- Weight and Size
Possible Flow Options For Liquid Cold Plate:
There are various kinds of possible flow options for a liquid cold plate that is designed for different types of Machines functionality. If you are facing any difficulty with flow options of liquid cold plates, we are here to solve your problem.
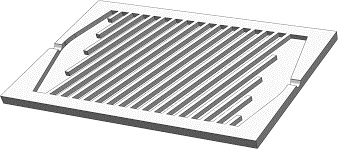
We design some best liquid Cold plate flow options for you. You can choose the best fluid option for the liquid cold plate according to your device’s requirements and functionality. Some possible flow options for liquid cold plates are given below.
- Micro-channel.
- Mini-channel.
- Manifold tube.
- Serpentine tubes are available.
Materials and Fluid Options:
For optimum heat transfer, the right and best fit working fluid and material must be chosen carefully for the efficient working of the device. Although the type of fluid varies according to the device requirements, the fluid must be high heat conductivity to manage the heat of high-powered devices.
The fluids that are most commonly used are water and glycol.
Water has better heat transfer capability, but tap water is not used because tap water contains many contaminants which cause problems for the device. Only high-quality water or deionized water is used for this purpose.
A mixture of water and glycol can be used because glycol has the ability to reduce temperature. For this purpose propylene glycol and ethylene glycol are used. Dielectric Fluids can also be used as fluid options to reduce temperature.
The materials which can be used in a cold plate system are mostly alloys. They can be:
- Aluminum.
- stainless steel.
- Copper.
- Polymer-based material.
Conclusion
A well-known method for transferring heat from your gadget is liquid cold plates. If you have any questions about liquid cold plates and their manufacturing process, don’t hesitate to get in touch with us. We’ll help you choose the liquid cold plates that best suit the functionality of your device, contact us for further queries.
Obviously, you are in the right place if you are looking for a good quality manufacturer of liquid cold plates. We designed the liquid cold plate in such a way that it helps you deal with complex issues of heat transfer from your device without affecting your device’s functionality.
