If you’re a business buyer, you know the importance of choosing the right heat sink for your needs. Choosing the right heat sink is very important, however, there are so many options that selecting among them could be a challenging task.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know about heat sinks, including what they are, how they work, and the different types available. We’ll also give you tips on how to choose the best one for your specific application.
So whether you’re looking for your first heat sink or just want to learn more about this essential component, read on!
What Is a Heat Sink?
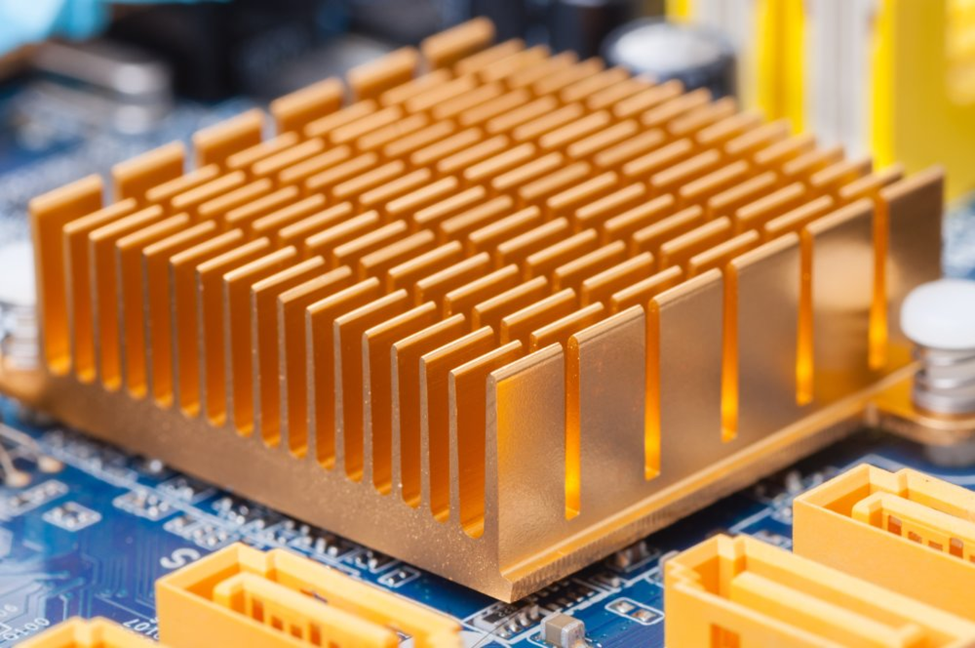
Heat sink is one of the essential components that is used in various devices that are used daily. These devices could produce a lot of heat while working, if they are not taken care of in case of temperature, overheating may ruin them. Also, the speed is highly impacted without a heat sink. A heat sink is a device that transfers heat from electronic components and prevent overheating. By transferring heat away from sensitive components, heat sinks help to extend the lifespan of electronic devices and ensure optimal performance.
Almost all kinds of electronic appliances and devices that are manufactured in the times of today are backed with a heat sink to ensure proper functioning. The flow of heat is directed away from the component itself and this is how the devices get rid of high temperature.
How Do Heat Sinks Work?
Heat sinks are commonly made up of materials like aluminum and copper and work as the best thermal conductors. The heat sinks absorb heat from the component that produces it and takes it away to a zone of broader surface area.
The heat spreads this way and reaches the fins, where the cooling starts. The heatsink is backed with a cooling fan that carries out the process of heat dissipation very perfectly.
The installation of heatsink was relatively considered in the huge computers used for carrying out particular tasks. However, nowadays, due to the high-speed demand for all kinds of devices, installing heat sink into them has become quite common.
In the absence of heat sinks, the process of performing operations by different devices could be hindered. Also, such devices may get damaged sooner or later due to extreme heat release.
The Different Types of Heat Sinks
There are three common types of heatsinks that are used in most of the devices, and these include the following:
Passive Heat Sinks
Passive heat sinks do not have a mechanical methodology to work with nor have any mechanics in its construction. They work with the help of radiators which are made with aluminum fins. The flow of heat is diverted using a convection process that leads to the cooling of surroundings.
The most significant advantage of choosing passive heat sinks is that they do not need any secondary power to work. However, as far as their effectiveness is concerned, they might lack compared to the active heat sinks.
Active Heat Sinks
The working mechanisms of active heat sinks are highly dependent on the cooling fans, and they require a secondary power to work. These could also be called cooling fans and blow away the heat using the forced air from the fan.
The efficiency of active heat sinks is commendable. They are very efficient and quickly divert the heat away from the critical components. However, since they have moving parts, they might lack longevity in life, and replacement is quite expensive.
Hybrid Heat Sinks
Hybrid heat sinks as the name suggests has some features of passive heat sink and some of the active heat sinks. They have specific features from the passive heat sinks and certain features from the active heat sinks.
They work using the mechanism when the device is not releasing much heat, and they use the passive heat sink technique. However, as soon as the machine starts to release a lot of heat and turns out to have a high temperature, the active heat sink starts working and cools it down.
The above ones are the types of heat sinks that are based on the working mechanism. However, there could also be numerous other kinds of heat sinks that may vary in terms of their process and their purpose.
Aluminum heat sink, machining heat sink, skived heat sink, forged heat sink, die cast heat sink, heat pipe heat sink and many more forms of heat sinks are also manufactured. They serve different purposes for different devices.
Applications of Heat Sinks
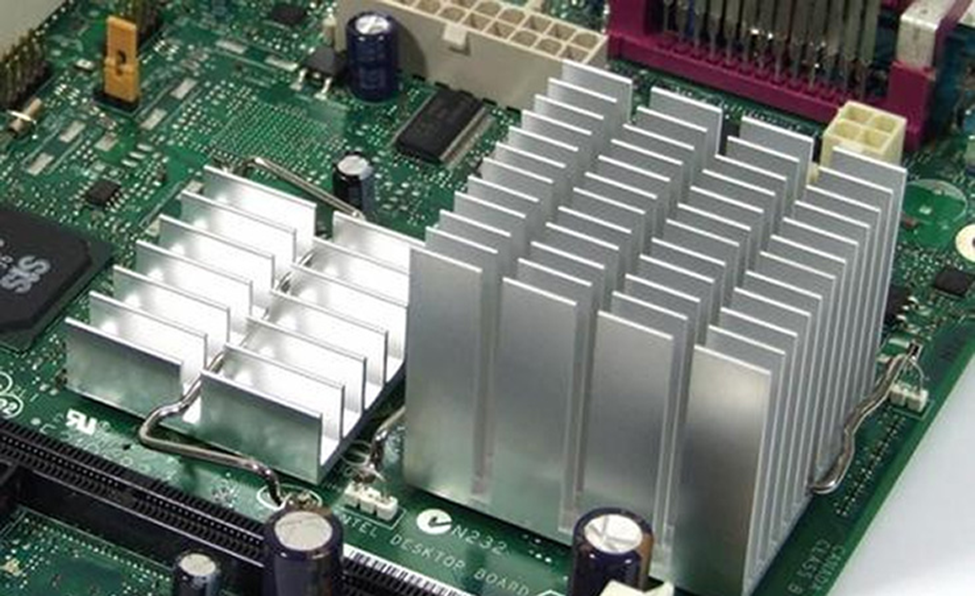

Heat sinks are used in almost all equipment. The main purpose of having heat sinks is to keep the heat away from the critical components of the device. Hence this way, the life and working capability of the devices also improve. There are numerous applications of heat sinks and some may include the following:
Server
A server, like any other computer, generates heat as a by-product of its normal operations. This heat can build up inside the server, causing it to overheat and potentially leading to damage. A heat sink helps to transferring heat, preventing the server from overheating. In addition, a heat sink can also help to extend the life of the server by preventing components from being damaged by excessive heat.
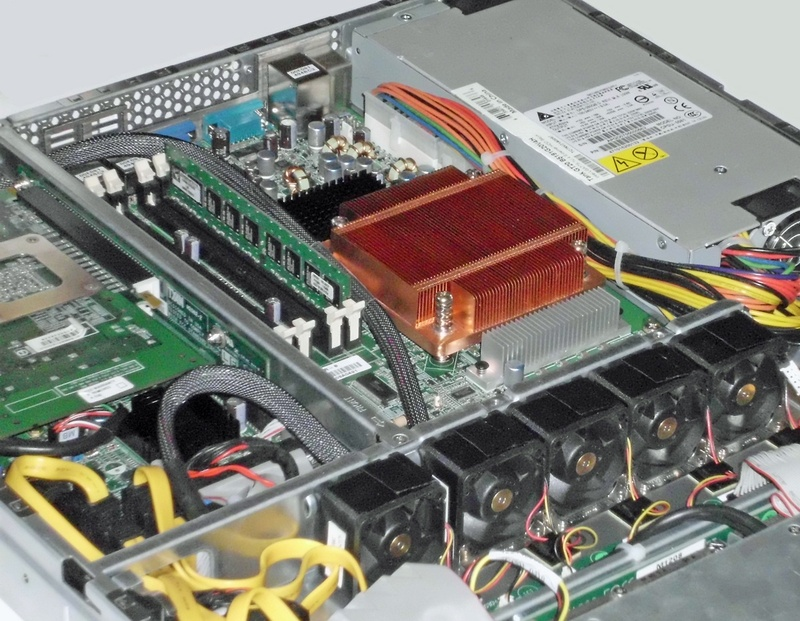
Data Center
Data center operators need to take many factors into consideration when designing their facilities, including power requirements, cooling needs, and network infrastructure. With so much focus on these high-level concerns, it can be easy to overlook the importance of choosing the right heat sink for data center servers. However, the heat sink is a critical component in server performance and reliability. When choosing a heat sink for a data center server, it is important to consider the size and airflow of the unit, as well as the operating temperature range. By carefully selecting a heat sink that meets the specific needs of the data center, operators can ensure that their servers will run cooler and more efficiently.
Automotive
Automotive electronics are constantly being improved to provide a safer, more comfortable and efficient driving experience. However, as electronic components become smaller, faster and more powerful, they generates heat on increasing levels . If this heat is not dissipated effectively, it can lead to component failure. This is where heat sinks come in. Heat sinks are designed to absorb and dissipate excess heat, preventing it from damaging sensitive electronic components. They are used extensively in automotive electronics, and their use is likely to increase in the future as electronic systems become more sophisticated.
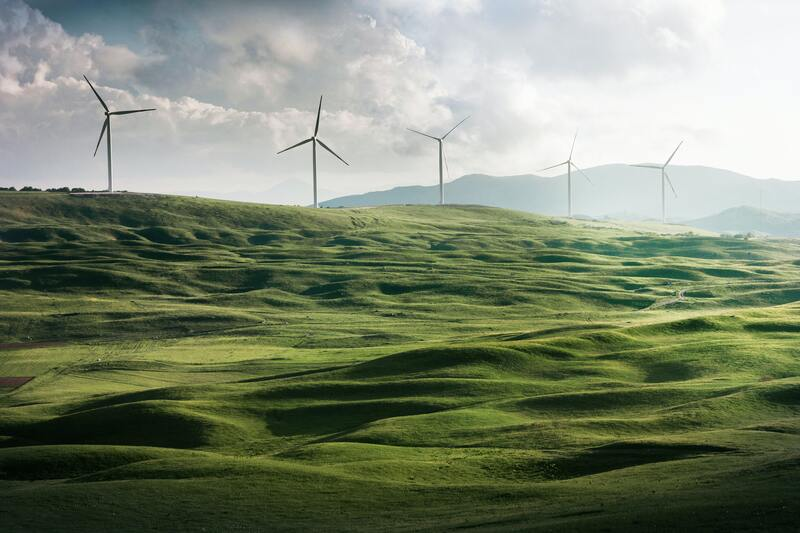
New Energy
Any device that needs to be cooled, whether it is an electronic unit or a machine, requires a heat sink. When it comes to new energy devices, such as solar panels and wind turbines, a heat sink is even more important. These devices are constantly generating electricity, and the resulting heat can quickly damage the delicate components. By attaching a heat sink, it is possible to keep the temperature of these components within safe limits. In addition, attaching a heat sink can also help to improve the overall efficiency of the device by keeping it cooler.

Photovoltaic Industries
As the global demand for renewable energy increases, so does the need for efficient and reliable photovoltaic (PV) systems. PV cells convert sunlight into electrical energy, and while this process is relatively simple in theory, it can be difficult to achieve in practice. One of the challenges facing PV cells is heat build-up. When exposed to sunlight, the cells can become very hot, which can reduce their efficiency and cause them to break down over time. Heat sinks are designed to dissipate heat away from the PV cells, keeping them cool and preventing damage. Without a heat sink, the PV cells would quickly overheat and stop working properly. As such, heat sinks are an essential unit of any photovoltaic system.
LED
The electronic devices based on Laser and LED units, the emission of heat from such devices is also very high; hence, heat sink transfers are significant. Therefore, the LED devices are also backed with heat sinks to keep the heat away from them.
Semiconductors
Heat sinks are also very commonly used in semiconductors because some high-powered ones may need heat transfer mechanisms. Hence, the cooling of semiconductors like transistors is frequently carried out with the help of a heat sink.
Consumer electronics
Most electronic devices generate heat when they are in use. While this is not necessarily a problem, it can become an issue if the heat is not properly dissipated. If too much heat builds up, it can damage the components of the device or cause it to malfunction. This is why consumer electronics need a heat sink. A heat sink helps to dissipate the heat generated by the device, keeping it within a safe temperature range. Without a heat sink, the components of the device would be at risk of overheating and failing. In addition, a heat sink can also help to prolong the life of the device by preventing premature wear and tear. As a result, consumer electronics need a heat sink in order to function properly and safely.
Conclusion
Heat sinks prove to be one of the essential components installed on different kinds of devices. Even if you consider the example of a CPU, you could conclude that the significance of a heat sink is undeniable.
If the heat sink is not installed, the cooling of the CPU would be hindered, and this will not only have an impact on the performance of the CPU but will also damage the surrounding components.
Hence, the presence of heat sinks is commonly observed on almost all devices that tend to release heat to keep the flow of heat controlled.
