Introduction
When we turn on our LED lights, they brighten our world, but did you know they also generate heat? Like you get warm when you exercise, LED lights get hot when they work. This heat can be a problem because if it gets too hot, the LED lights might not shine as brightly or could even stop working. That’s where the heat sink design comes in!
Think of a heat sink like a superhero cape for LED lights. It’s a special part designed to help LED lights stay cool by absorbing and spreading away the extra heat. In this guide, we’ll explore how heat sinks work, the different types of heat sinks, and how to choose the right one.
We’ll also learn about materials that make heat sinks super effective and cool tricks like heat pipes and liquid cooling. So, get ready to discover the secrets of keeping LED lights shining bright with the power of heat sink design!
Fundamentals of Heat Sink Design
What Is a Heat Sink and Its Role?
Imagine you’re outside on a hot summer day and start feeling warm. You might jump into a pool or drink a cold beverage to cool down. In a way, your body is like an LED light because it can get hot when working hard. This is similar to LED lights – they produce heat when they shine.
A heat sink is like a superhero’s shield for LED lights. It’s a special part designed to help LED lights stay cool by removing the extra heat and spreading it away. So, when LED lights work, the heat sink keeps them from getting too hot and helps them perform their best. Think of it as a heat protector!
Types of Heat Sinks
Heat sinks come in different shapes and sizes. Some look like fins, while others are flat plates. There are also special heat sinks with fans built to blow away the heat. These different types are like different costumes for our LED superheroes – they all have the same mission: to keep things cool.
Heat Sink Material Selection and Thermal Conductivity
Picking the right material for a heat sink is crucial. It’s a bit like choosing the right tool for a job. Common materials are aluminium and copper because they’re great at spreading heat. We measure this ability with something called thermal conductivity – it’s like how quickly news travels.
Materials with high thermal conductivity can quickly move heat away from the LED, keeping it cool. So, choosing the right material is important in heat sink design.
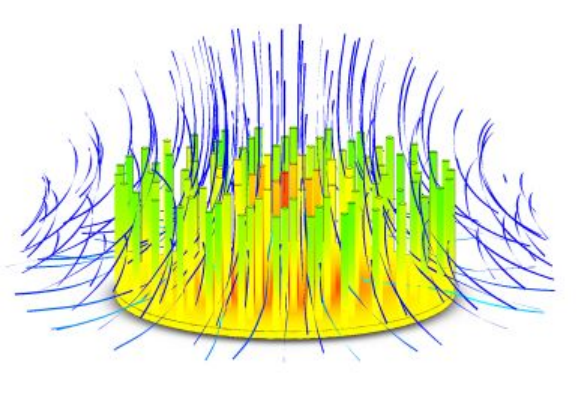
Key Design Considerations
Heat Sink Geometry and Size
Think about puzzles – they come in all shapes and sizes, like squares, circles, and triangles. Heat sinks are a bit like that. They can have different shapes, like fins or plates, and can be big or small.
Choosing the right shape and size is like finding the perfect puzzle piece that fits just right. The heat sink’s shape and size affect how well it can cool the LED. If it’s too small or the wrong shape, it won’t work as well.
Thermal Interface Materials (Tims)
Imagine you’re making a sandwich. You put some tasty ingredients between two slices of bread. TIMs are like the special stuff you put between the heat sink and the LED to help them stick together better. It’s like the mayonnaise or mustard in your sandwich.
TIMs ensure no gaps so the heat can flow smoothly from the LED to the heat sink. Using the right TIM is like using the right spread on your sandwich – it makes everything work better.
Mounting and Attachment Methods
How do you attach a poster to your wall? You might use tape, pins, or glue. We stick the heat sink to the LED by mounting and attachment methods. Some heat sinks use clips, screws, or special adhesive.
Choosing the right method is like picking the best way to hang your poster. If it’s not attached properly, the heat sink won’t work, and the LED could get too hot. So, getting this part right is super important for keeping things cool.
Calculating Heat Sink Requirements
Thermal Design Power (Tdp)
Imagine planning a trip and wanting to know how much gas your car will use. TDP is like that for LEDs. It tells us how much power an LED light uses and how much heat it generates. Knowing the TDP helps us determine how big or effective our heat sink needs to be to keep things cool. Like a bigger car might need more gas, a high TDP LED needs a more capable heat sink.
Junction Temperature and Maximum Ratings
It can feel warm when you touch your computer or phone after using it for a while. The same thing happens with LEDs – they get warm, too. Junction temperature is like the LED’s body temperature and shouldn’t get too hot.
We have maximum ratings, like a person’s highest safe body temperature. If the junction temperature goes above this limit, it can harm the LED’s performance or even damage it. So, keeping track of junction temperature and maximum ratings is vital for LED health.
Practical Heat Sink Sizing Examples
Imagine you have a pizza and want to know how many slices to cut it into so everyone gets enough. Practical heat sink sizing is like that for LED lights. We use the TDP and maximum ratings to determine the right heat sink size.
If the LED has a high TDP, we need a bigger heat sink, just like you’d need more pizza slices for a big group. Practical examples show us how to calculate the right size so the LED stays cool and works its best.

Advanced Heat Sink Technologies
Heat Pipes and Vapor Chambers
Think of heat pipes like magic wands for heat. They’re thin tubes filled with a special liquid that can quickly absorb heat from the LED. Imagine the liquid turning into a gas to carry the heat away, like water turning into steam.
Heat pipes are like the fast runners in a race, efficiently moving heat to keep things cool. Vapour chambers are like bigger versions of heat pipes, spreading the heat even more effectively, like a big umbrella protecting you from the sun.
Phase Change Materials (PCM)
PCMs are like secret coolers for LEDs. They’re special materials that can absorb heat as they change from solid to liquid. Think of it like an ice cube turning into water while keeping things chilly. PCMs can be placed near the LED, soaking up its heat and keeping it from getting too hot. It’s like having an ice pack to cool down a hot day.
Liquid Cooling Solutions
Imagine if your computer or car had a special liquid flowing to keep it cool. Liquid cooling solutions work like that for LEDs. They use liquid to carry heat away from the LED, like how your blood carries oxygen around your body.
Liquid cooling can be super effective at keeping LEDs cool, even when they work hard. It’s like having a built-in air conditioner for your lights, ensuring they shine brightly without overheating.
Thermal Testing and Validation
Measuring Temperature in LED Systems
To ensure our LED lights stay cool, we need to check their temperature, just like taking your temperature when you’re not feeling well. We use special tools, like thermometers, to measure the LED’s hot or cold. This helps us know if it’s getting too hot and if our heat sink works properly.
Conducting Thermal Testing and Interpreting Data
Doing thermal testing is like running experiments to see if our LED lights are staying cool enough. We collect data, like gathering information about the LED’s temperature and how well the heat sink works.
Then, we analyze or study that data to ensure everything is okay. It’s like checking your homework to see if you got all the answers right. If the data shows a problem, we can fix it to keep our LEDs shining brightly without overheating.
Future Trends and DIY Tips
Emerging Technologies and Materials
In the future, new and cool stuff will come into play to make LED lights even better. Think of it like getting the latest smartphone with new features. There will be fresh technologies and materials that can help LEDs stay super cool and work more efficiently. These innovations will make LED lights even more awesome.
Practical Tips for DIY Heat Sink Design
If you’re interested in making your heat sink, here are some handy tips to remember. Just like building a model or crafting, there are tricks and techniques you can learn. These practical tips will help you design a heat sink that works well and keeps your DIY LED project running smoothly without getting too hot. It’s like having a guide to create your superhero costume for your LED lights.
Conclusion
The world of LED lighting is not just about illumination; it’s also about managing the heat generated by these energy-efficient marvels. Heat sink design plays a pivotal role in ensuring the longevity and performance of LED lights. Think of it as the unsung hero behind the scenes, safeguarding your LEDs from overheating.
We’ve delved into the fundamentals of heat sink design, exploring their various types, materials, and critical considerations. Remember that choosing the right shape, size, material, thermal interface, and attachment method is akin to putting together the perfect puzzle for your LED setup.
Advanced technologies like heat pipes, vapor chambers, phase change materials, and liquid cooling solutions promise to revolutionize LED cooling, ensuring they shine brightly without sweat.
Looking ahead, the world of LED lighting holds exciting prospects with emerging technologies and materials on the horizon. And for the DIY enthusiasts, practical tips await to guide you in crafting your superhero costume for your LED lights. With the power of heat sink design, your LEDs can illuminate the future brilliantly and efficiently without ever losing their cool.
